Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) is a genetic disorder characterized by overgrowth and various associated conditions, impacting approximately one in 10,000 births. This overgrowth disorder can manifest through distinct symptoms like macrosomia, or excessive growth, and macroglossia, where the tongue is enlarged. Early prenatal diagnosis is essential, as identifying BWS symptoms can lead to better management and support for affected families. Children with this condition often face unique challenges, such as a higher risk of certain childhood cancers and asymmetrical growth known as hemihypertrophy. Understanding this complex syndrome is vital for expectant parents navigating potential concerns throughout their pregnancy journey.
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS), often referred to in medical contexts as an overgrowth condition, comprises a collection of genetic anomalies that typically surface in childhood. This syndrome is also known for its potential implications during prenatal assessments, where atypical growth patterns can raise flags for further evaluation. Families encountering these childhood syndromes may experience a whirlwind of emotions as they seek information on possible BWS symptoms and outcomes. Genetic disorders, such as BWS, serve as a reminder of the intricacies of human development, often requiring close monitoring and intervention. Preparing for a future with a child diagnosed with conditions like BWS necessitates a supportive network and thorough understanding to navigate the complexities ahead.
Understanding Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS)
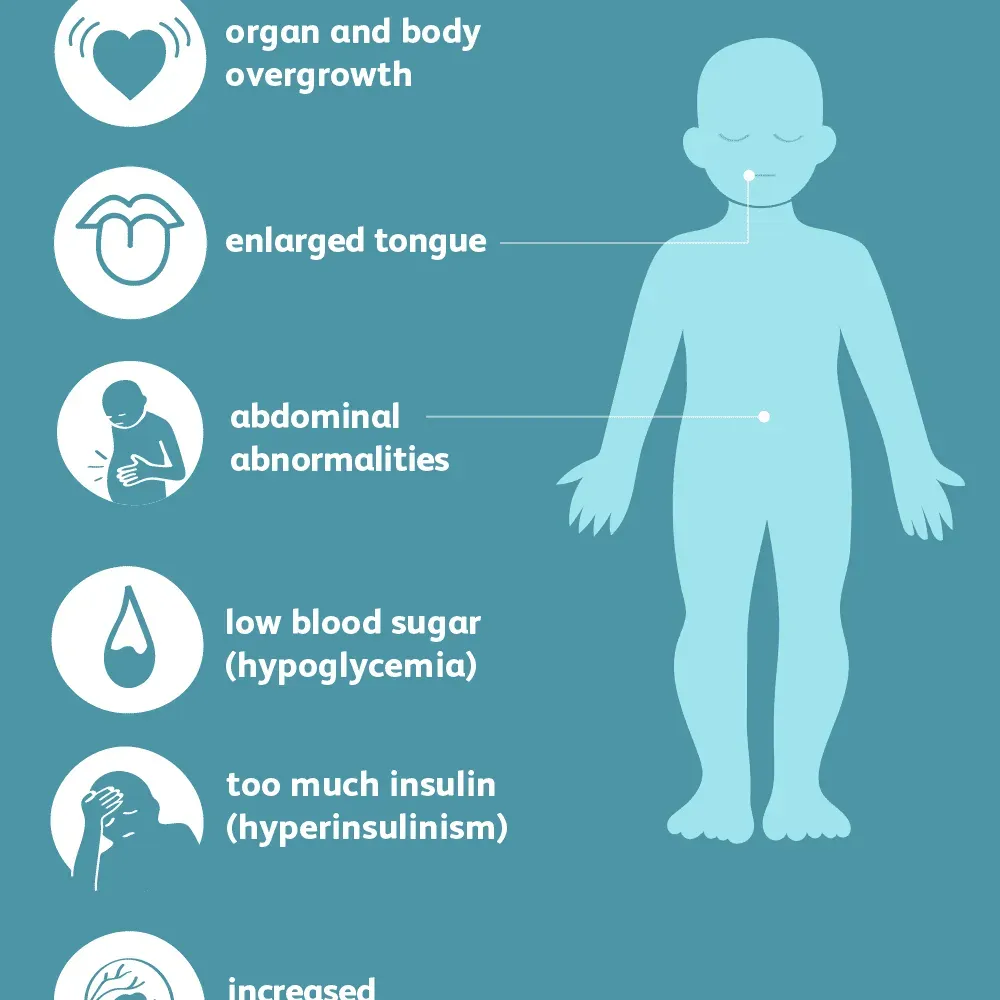
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) is a genetic disorder characterized by abnormal growth patterns and an increased risk of certain cancers in children. Typically diagnosed in childhood, this condition manifests through various physical traits. Common symptoms include macrosomia, where affected children are significantly larger than their peers, hemihypertrophy which refers to one side of the body growing more than the other, and macroglossia, an enlargement of the tongue that can hinder normal feeding and speech development. As a parent learning about BWS, it’s important to comprehend these characteristics not just to acknowledge the challenges they present, but also to understand the medical support that can be offered to ensure proper monitoring and care for your child’s health needs.
The journey of a parent encountering a diagnosis of Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome is often fraught with emotional upheaval. This overgrowth disorder can lead to a host of complications, making early detection and management crucial. In particular, the elevated risk of childhood cancers associated with BWS requires vigilant health surveillance. Parents should actively engage with pediatric specialists and genetic counselors to formulate a tailored care plan that can include regular imaging and developmental assessments. The psychological and emotional impact of this syndrome extends beyond its physical symptoms; recognizing and addressing these aspects through support groups or counseling can be invaluable for families navigating this path.
The Symptoms and Features of BWS
When it comes to understanding Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome, it’s essential to familiarize oneself with its symptoms and features. Apart from the hallmark characteristics of macrosomia, hemihypertrophy, and macroglossia, children diagnosed with BWS may also present with distinctive facial features such as pink capillary malformations on their foreheads. Additionally, developmental irregularities may occur, including abdominal wall defects that can lead to serious complications. These features emphasize the complexity of this genetic disorder, making it critical for affected individuals to have access to specialized healthcare for comprehensive management.
For families, recognizing the various manifestations of BWS can be both a relief and a source of anxiety. The myriad symptoms mean that while no two children will present identically, the potential for comorbidities can be overwhelming. This is where thorough prenatal diagnosis and early intervention come into play, ensuring that families are prepared for the unique journey ahead. Regular check-ups and interdisciplinary coordination among healthcare providers can significantly improve the quality of life for children with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome.
Navigating Genetic Disorders and Their Impact
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome sits among a spectrum of genetic disorders that can profoundly shape a child’s early development. Understanding the genetic basis of BWS allows parents and caregivers to better advocate for their child’s health needs. Genetic testing can provide clarity around the condition, helping families grasp the implications for future siblings and inform reproductive choices moving forward. This knowledge is crucial not only for parents but also for healthcare providers who offer insights into the condition’s likely course over time.
Moreover, the emotional landscape surrounding diagnosis in genetic disorders, such as BWS, is often complex. Feelings of fear, anxiety, and isolation can be common. However, connecting with other families facing similar challenges can foster support and resilience. Online communities and advocacy groups serve as essential resources, enabling sharing of experiences, coping strategies, and recommendations for specialized care. Navigating the landscape of a genetic disorder like Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome calls for both emotional and practical preparedness, highlighting the importance of community and support.
Prenatal Diagnosis: Early Detection and Its Importance
The advancement of prenatal diagnosis has revolutionized how conditions like Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome are understood and managed. Non-invasive tests such as ultrasounds can sometimes reveal physical indications of BWS, while amniocentesis and other genetic tests can provide definitive answers. Early detection comes with its own set of challenges, particularly in managing the emotional response of expectant parents. Although knowledge of a potential disorder can prepare families, it can also lead to anxiety as they contemplate their child’s future.
However, with early diagnosis comes the opportunity for informed decisions regarding care. Post-natal interventions might include specialist consultations and developmental assessments that can mitigate long-term complications associated with BWS. Being proactive during pregnancy with regular screenings and open dialogue with healthcare professionals is vital in ensuring the right support is available when the child is born. Knowledge gained through prenatal diagnosis can empower families to create action plans that prioritize their child’s health from day one.
Overgrowth Disorders: More Than Just Physical Size
While on the surface, Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome and other overgrowth disorders may seem primarily defined by physical characteristics, the realities of living with such conditions are multifaceted. These disorders can impact cognitive and emotional development, leading to challenges that extend beyond the scale. For instance, children with BWS may face learning disabilities or social difficulties rooted in their unique appearance and associated health issues. Understanding that overgrowth can affect all aspects of a child’s life is crucial for parents seeking comprehensive care.
Moreover, supportive interventions can play a critical role in helping children thrive. Occupational and speech therapy may be beneficial in addressing limitations arising from BWS symptoms such as macroglossia. Early intervention services and personalized learning strategies in educational settings can aid in addressing developmental delays. As families navigate the complexities of these overgrowth disorders, fostering strength in emotional resilience and adaptability can empower both the child and the family unit.
Connecting with Online Communities: A Source of Comfort
In our digital age, social media and online forums have become invaluable resources for families facing unique health challenges like Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome. These platforms provide spaces for individuals and parents to share personal stories, challenges, and triumphs related to managing such conditions. The ability to connect with others who understand the emotional and logistical facets of BWS can provide a sense of belonging and reassurance, particularly during isolating moments.
Engaging with online communities not only offers emotional support but also facilitates information exchange. Members can recommend specialists, therapies, and coping strategies based on trial and error, helping families navigate a complex healthcare system. The shared sense of community can be therapeutic in itself, lessening the burden of fear and uncertainty for parents. Through shared experiences, families can also participate in advocacy efforts aimed at improving awareness and research surrounding genetic disorders such as Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome.
The Role of Genetic Counselors in Managing BWS
As parents come to terms with a diagnosis of Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome, the role of a genetic counselor becomes pivotal. These trained professionals provide guidance on understanding the genetic implications of BWS, educating families on inheritance patterns and risks for future pregnancies. They offer a safe space to voice concerns, ask questions, and explore the emotional responses associated with genetic diagnosis. Moreover, genetic counselors can help families navigate the often overwhelming array of medical information and connect them with appropriate resources.
Furthermore, genetic counseling can offer long-term support, helping families adjust their understanding and expectations as their child grows. They can assist in creating a comprehensive care plan tailored to the child’s unique needs, including frequent check-ups and referrals to specialists such as endocrinologists and oncologists when necessary. By facilitating a family-centered approach to care, genetic counselors play a crucial role in ensuring that parents feel empowered to make informed decisions that ultimately foster their child’s well-being.
Coping with Emotional Turmoil: Strategies for Parents
Receiving a diagnosis like Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome can usher in a wave of complex emotions for parents, ranging from denial to deep despair. Understanding that these feelings are normal and part of a grief process for the anticipated ‘normal’ child can help in validating one’s emotional experience. Seeking support from mental health professionals and participating in therapy can be instrumental in coping with the fears that accompany living with a genetic disorder. Support groups, where parents can connect and share their stories, can also ease feelings of isolation.
Additionally, engaging in self-care practices can provide much-needed respite and clarity for parents navigating this emotional journey. Setting aside time to process feelings, taking care of physical health, or simply reaching out for help when overwhelmed can significantly reduce stress. The path ahead may be uncertain, but embracing community support and prioritizing mental and emotional wellness allows parents to better advocate for their children while building resilience for themselves.
Long-Term Outcomes and Support for BWS
The long-term outcomes for children with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome largely depend on early detection and comprehensive care. With proper medical oversight, many individuals can lead healthy lives, managing any complications effectively. Routine monitoring for associated risks, such as that of childhood cancer, plays a critical role in improving survival and the quality of life for these children. The importance of establishing a proactive care team, including specialists, is essential for maintaining health and fostering positive development.
Additionally, ongoing support for families is vital as children with BWS navigate various life stages. Educational accommodations, therapeutic interventions, and community resources can significantly enhance their quality of life. As awareness grows, so does the importance of advocating for research into Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome to develop improved treatment protocols and interventions. By investing in their future, families contribute to broader efforts aimed at understanding and supporting children with genetic disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS)?
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) is characterized by several symptoms, including macrosomia (excessive growth), hemihypertrophy (asymmetrical growth), and macroglossia (enlarged tongue). Children with BWS may also exhibit ear creases, pink capillary abnormalities on the forehead, and in some cases, an abdominal wall defect leading to organ displacement. Early diagnosis and monitoring are crucial due to the elevated risk of certain childhood cancers.
How is Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome diagnosed before birth?
Prenatal diagnosis of Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) typically involves a combination of detailed ultrasound examinations and genetic testing. During routine scans, doctors may observe indicators such as excessive fetal growth or macroglossia. If concerns arise, they may recommend an amniocentesis to analyze fetal DNA for genetic markers associated with BWS, helping to confirm the diagnosis before birth.
What are the potential complications associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome?
Children with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome may face several complications, including an increased risk of certain childhood cancers, particularly Wilms tumor and hepatoblastoma. Other potential issues include feeding difficulties due to macroglossia and challenges associated with asymmetrical growth. Regular monitoring by healthcare providers is essential to manage these risks and provide appropriate interventions.
Can adults have Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome, or is it only a childhood syndrome?
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) is primarily recognized as a childhood syndrome, as its most significant manifestations are observed during early development. However, individuals with BWS can continue to experience health issues into adulthood, including a higher risk of certain cancers and the need for ongoing medical supervision. Early diagnosis and care are critical in managing the long-term implications of BWS.
What genetic factors are associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome?
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) is often linked to genetic alterations, particularly Imprinting Disorders affecting genes on chromosome 11p15. Most cases of BWS result from changes in genomic imprinting, which affects how genes are expressed. Mutations in specific genes such as CDKN1C and changes in methylation patterns can also play a role in the development of this overgrowth disorder.
Is there a specific treatment for Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome?
Currently, there is no cure for Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS), and treatment typically focuses on managing the symptoms and complications associated with the disorder. This may include surgical interventions for physical abnormalities, regular monitoring for the early detection of potential cancers, and supportive therapies to aid development and address feeding issues.
How does Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome impact a child’s development?
Children with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) may experience developmental challenges depending on the severity of their symptoms. While many children can achieve typical developmental milestones, some may need additional support in areas such as speech, feeding, and coordination. Early intervention programs and continuous care from healthcare professionals can significantly benefit their growth and development.
What resources are available for families affected by Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome?
Families dealing with Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS) can access a variety of resources, including support groups, online communities, and informational websites that provide guidance on managing the syndrome. Organizations such as the Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome Support and Advocacy Association offer valuable information, connect families with experts, and foster a supportive network for sharing experiences and resources.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The author discovered potential issues with their unborn child during a routine ultrasound, leading to concerns about Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS). |
| BWS is a rare overgrowth disorder that affects 1 in 10,000 births, typically manifesting in childhood. |
| Common features of BWS include macrosomia, hemihypertrophy, macroglossia, and a higher risk of childhood cancers. |
| Traditional pregnancy resources offered limited support or information for expecting parents dealing with complex syndromes like BWS. |
| The reaction to the diagnosis can lead to confusion and fear, particularly with alarming information found online. |
Summary
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome is a complex condition that can cause significant anxiety for expecting parents upon diagnosis. The journey from uncertainty in pregnancy to understanding the specifics of this disorder is often filled with fear and confusion. Parents facing BWS must navigate a web of information and emotions, especially as they seek reassurance and community support through platforms like social media. Understanding the characteristics and challenges of Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome can help in finding the right resources and support systems.