Exploring The Balance Of Power In Government is a complex and critical topic that involves the distribution of authority and influence among different branches of government. This balance of power is essential for preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful and potentially abusing its authority. The concept of checks and balances, separation of powers, and the role of each branch in the decision-making process are all central to understanding the balance of power in government.
One aspect of the balance of power in government that piques interest is the relationship between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. This dynamic is crucial in ensuring that each branch operates within its constitutional limits and serves as a check on the others. Additionally, the role of independent agencies and the influence of public opinion on the balance of power are also intriguing areas of exploration. Understanding how different factors interact to maintain a stable balance of power is essential for a well-functioning government.
The Concept of Balance of Power in Government
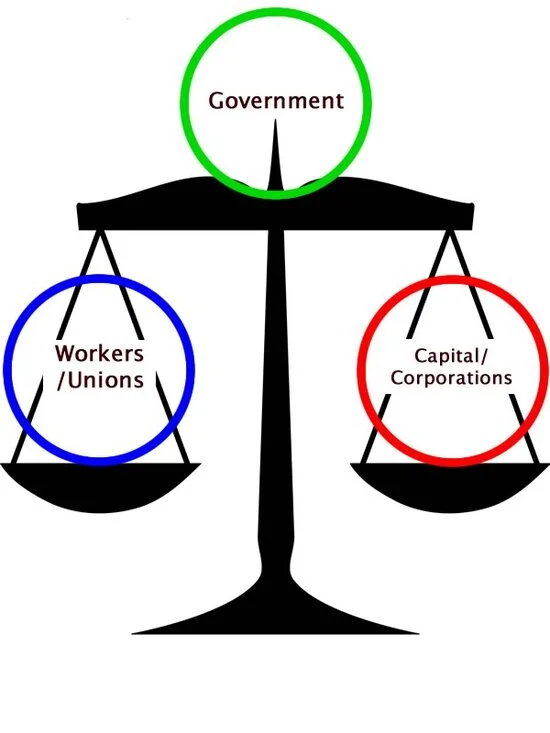
The balance of power in government refers to the distribution of political and institutional power among different branches and levels of government. This concept is based on the idea of preventing any one branch or level of government from becoming too powerful and potentially abusing that power. In a system with a balance of power, each branch or level of government has certain checks and balances over the others, which helps to ensure that no single entity has unchecked authority. This concept is fundamental to the idea of separation of powers, which is a key principle in many democratic systems.
The balance of power in government is often achieved through mechanisms such as the separation of powers, the system of checks and balances, and federalism. These mechanisms are designed to ensure that no single branch or level of government can dominate the others, and that each has a role in the decision-making process. By distributing power in this way, the system aims to prevent the concentration of power in the hands of a few, and to promote accountability and transparency in governance. The balance of power is a crucial aspect of democratic governance, as it helps to safeguard against tyranny and abuse of power.
Separation of Powers
The principle of separation of powers is a key component of the balance of power in government. This principle divides the functions of government into three separate branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The legislative branch is responsible for making laws, the executive branch is responsible for implementing and enforcing laws, and the judicial branch is responsible for interpreting laws and ensuring their constitutionality. By separating these powers, the system aims to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful and infringing on the authority of the others.
The separation of powers also includes checks and balances, which allow each branch to limit the power of the others. For example, the legislative branch may have the power to impeach the president, the executive branch may have the power to veto legislation, and the judicial branch may have the power to declare laws unconstitutional. These mechanisms help to ensure that no single branch can dominate the others, and that each has a role in the governance of the country.
System of Checks and Balances
The system of checks and balances is a fundamental feature of the balance of power in government. This system allows each branch of government to have some measure of influence over the other branches, which helps to prevent any one branch from becoming too powerful. For example, the president may have the power to veto legislation passed by Congress, but Congress can override the veto with a two-thirds majority vote. Similarly, the judicial branch has the power to interpret laws and declare them unconstitutional, but the president appoints federal judges with the approval of the Senate. These examples illustrate how each branch has the ability to check the power of the others, which helps to maintain a balance of power in the government.
The system of checks and balances is designed to prevent the abuse of power and to promote cooperation and compromise among the branches of government. By giving each branch some measure of control over the others, the system aims to ensure that no single branch can act without accountability, and that decisions are made through a process of negotiation and consensus-building. This system is a crucial component of democratic governance, as it helps to uphold the principles of liberty, equality, and justice.
Federalism
Federalism is another important element of the balance of power in government. This system divides power between a central, national government and smaller, regional governments such as states or provinces. In a federal system, each level of government has its own set of powers and responsibilities, and neither can abolish the other. This division of power helps to prevent the central government from becoming too dominant, and allows for a more localized approach to governance.
Federalism also serves as a check on the power of the central government, as the regional governments have certain powers that are independent of the national government. For example, states in the United States have the authority to pass their own laws on certain matters, such as education and transportation, which allows for a degree of autonomy and diversity in governance. This system of federalism helps to ensure that power is not concentrated solely at the national level, and that different regions have some measure of control over their own affairs.
The Role of Political Parties
Political parties play a significant role in the balance of power in government, as they are key actors in the legislative branch and the executive branch. In many democratic systems, political parties compete for control of the government through elections, and the party or coalition that holds the majority of seats in the legislature often has a significant influence over the direction of policy and governance. This influence can either help maintain the balance of power or potentially disrupt it, depending on the distribution of power among the branches and levels of government.
In some cases, political parties may also serve as a check on the power of the executive branch, particularly if the legislature is controlled by a different party. This scenario can lead to a system of divided government, where different branches are controlled by different parties, which can result in a more balanced distribution of power and a greater degree of oversight and accountability. However, political parties can also contribute to power struggles and gridlock if they are unable to cooperate and compromise in the governance process.
The Influence of Special Interest Groups
Special interest groups, also known as lobbies, can have a significant influence on the balance of power in government. These groups represent specific interests or industries and seek to influence government policy and decision-making in favor of their members. Special interest groups can exert influence through various means, such as lobbying elected officials, funding political campaigns, and engaging in grassroots advocacy. Their influence can potentially tip the balance of power in favor of certain interests over others.
While special interest groups are a natural part of the democratic process and have the right to petition the government, their influence can also raise concerns about the equitable distribution of power. If certain groups are able to exert disproportionate influence on government decision-making, it can undermine the principle of a balanced and representative democracy. Therefore, it is important for the balance of power in government to also consider the influence of special interest groups and to ensure that decision-making processes are transparent and accountable to the broader public interest.
The Role of the Judiciary
The judiciary plays a crucial role in upholding the balance of power in government through its authority to interpret and enforce the law. In many democratic systems, the judiciary is an independent branch of government that has the power to review the actions of the legislative and executive branches, and to ensure that they comply with the constitution. This authority serves as a check on the power of the other branches and helps to maintain a balance of power in the government.
The judiciary’s role in interpreting the law and resolving disputes also contributes to the balance of power by providing a mechanism for resolving conflicts between different branches or levels of government. Through its decisions, the judiciary can help to clarify the boundaries of authority and ensure that no single branch or level of government oversteps its constitutional limits. This role is essential in safeguarding the principles of democracy, the rule of law, and the protection of individual rights and liberties.
The Impact of Historical and Cultural Factors
Historical and cultural factors can have a significant impact on the balance of power in government. The development of political institutions, the distribution of power among different branches and levels of government, and the role of political actors are often influenced by a country’s historical experiences and cultural values. For example, countries with a history of authoritarianism may have a different balance of power compared to countries with a tradition of democratic governance. Similarly, cultural values such as individualism, collectivism, or the role of religion can shape the distribution of power and the dynamics of governance.
Understanding the impact of historical and cultural factors is essential for analyzing the balance of power in government, as it provides insight into the unique challenges and opportunities that each country faces in maintaining a balanced and effective system of governance. By considering these factors, policymakers and citizens can work towards creating a balance of power that reflects the values and aspirations of the society, and that promotes stability, justice, and prosperity for all.
| Branch | Role |
|---|---|
| Executive | Enforces laws |
| Legislative | Makes laws |
| Judicial | Interprets laws |