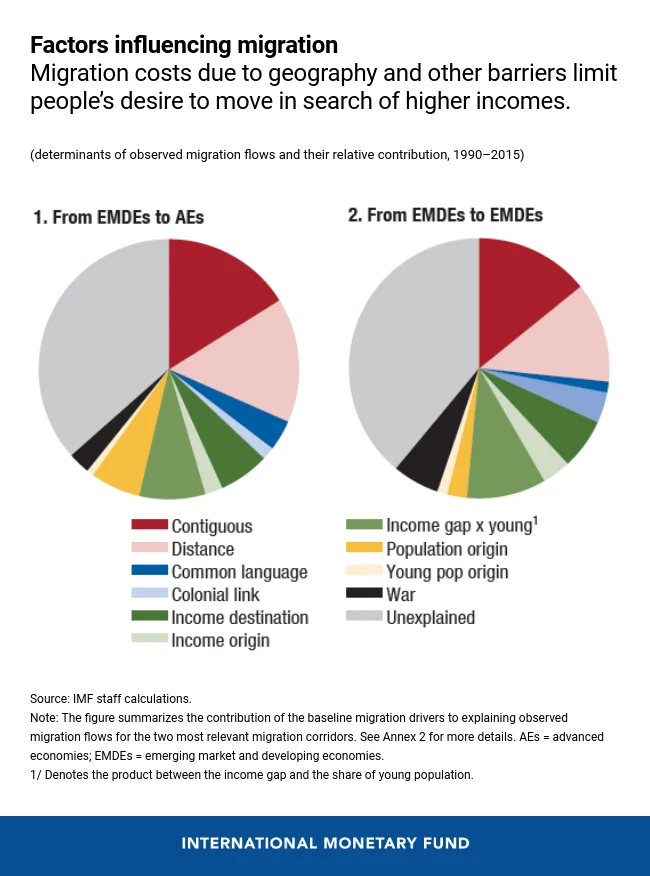
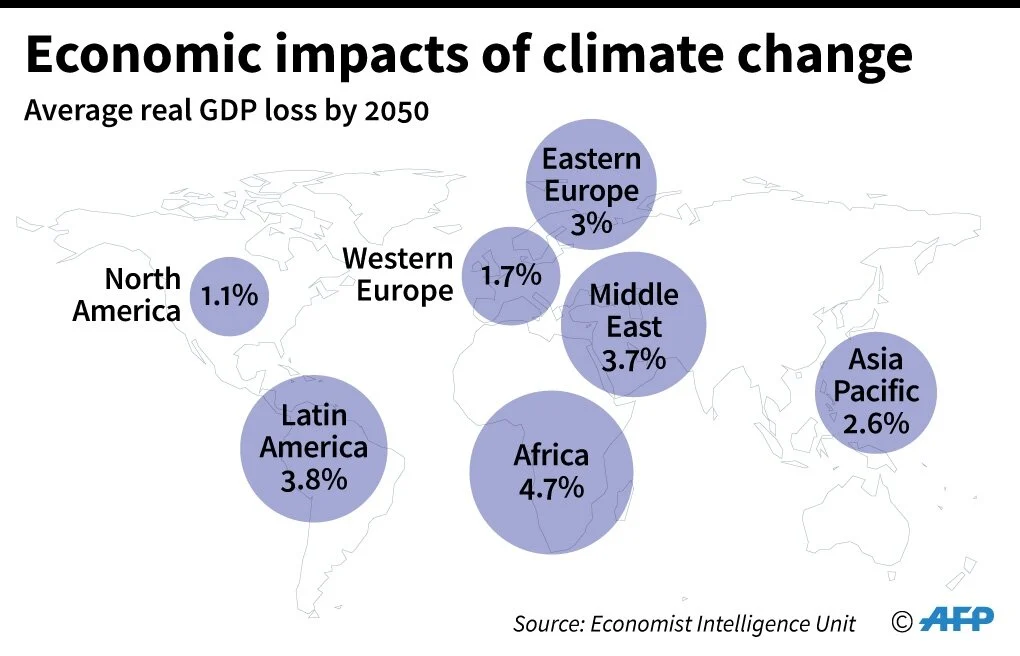
How Immigration Policies Affect Economies
Immigration policies play a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of countries. The influx of skilled workers from abroad can significantly contribute to the growth and innovation of domestic industries. Additionally, policies that streamline the integration of immigrants into the workforce can lead to increased productivity and competitiveness. On the other hand, restrictive immigration policies may limit the labor pool and hinder economic growth. Moreover, the impact of immigration policies on the labor market, wages, and public finances cannot be overlooked. Therefore, understanding how immigration policies affect economies is essential for informed decision-making and sustainable development.
The economic implications of immigration regulations are a subject of great interest and curiosity. Many are eager to comprehend the correlation between immigration policies and job opportunities, as well as the influence on wage levels. Furthermore, there is a growing concern about the potential effects of immigration policies on the welfare system and public expenditure. It is also intriguing to explore how immigration policies can shape the demographic structure and consumer market of a country. Overall, the multifaceted impact of immigration policies on economies sparks various questions and prompts a deeper exploration of the topic.
1. Labor Market Impact
Immigration policies have a significant impact on labor markets in host countries. When immigration policies are restrictive, it can lead to labor shortages in certain industries, which in turn can hinder economic growth. On the other hand, more open immigration policies can help address these shortages by providing a larger pool of workers. This can lead to increased productivity and economic output as businesses are able to find the necessary labor to meet demand. However, it is important to note that immigration policies can also affect the wages of native workers, as an influx of immigrant workers can sometimes lead to increased competition for jobs and potentially lower wages in certain sectors.
Additionally, immigration policies can also impact the skill composition of the labor force. For example, policies that prioritize high-skilled immigration can lead to a more skilled workforce, which can have positive implications for innovation and economic competitiveness. Conversely, policies that restrict immigration to only low-skilled workers may lead to shortages in industries that rely on this type of labor, ultimately impacting the overall economic performance of the country.
2. Economic Growth and Innovation
Immigration policies play a crucial role in shaping a country’s economic growth and innovation. By attracting skilled immigrants, countries can benefit from the knowledge and expertise brought in by these individuals, leading to greater innovation and technological advancements. These contributions can have a positive impact on various industries, including science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM), which are critical drivers of economic growth. Furthermore, immigrants often start businesses at a higher rate than native-born citizens, leading to job creation and economic stimulation.
On the other hand, restrictive immigration policies can limit the influx of talent and innovation, potentially hindering a country’s ability to remain competitive in the global economy. By creating barriers to skilled immigration, countries may miss out on the opportunity to harness the full potential of a diverse and talented workforce, ultimately impacting their ability to innovate and grow economically.
| Immigration Policy | Economic Impact |
|---|---|
| Open Borders | Increases labor force, promotes innovation, and boosts economic growth. |
| Strict Border Control | Limits labor force growth, may lead to labor shortages in certain industries, and hinders economic expansion. |
| Skilled Immigration Preference | Brings in highly skilled workers who contribute to technological advancements and economic productivity. |
| Family-Based Immigration Preference | May lead to higher immigration numbers, potentially straining public resources, but also contributes to consumer demand and economic activity. |