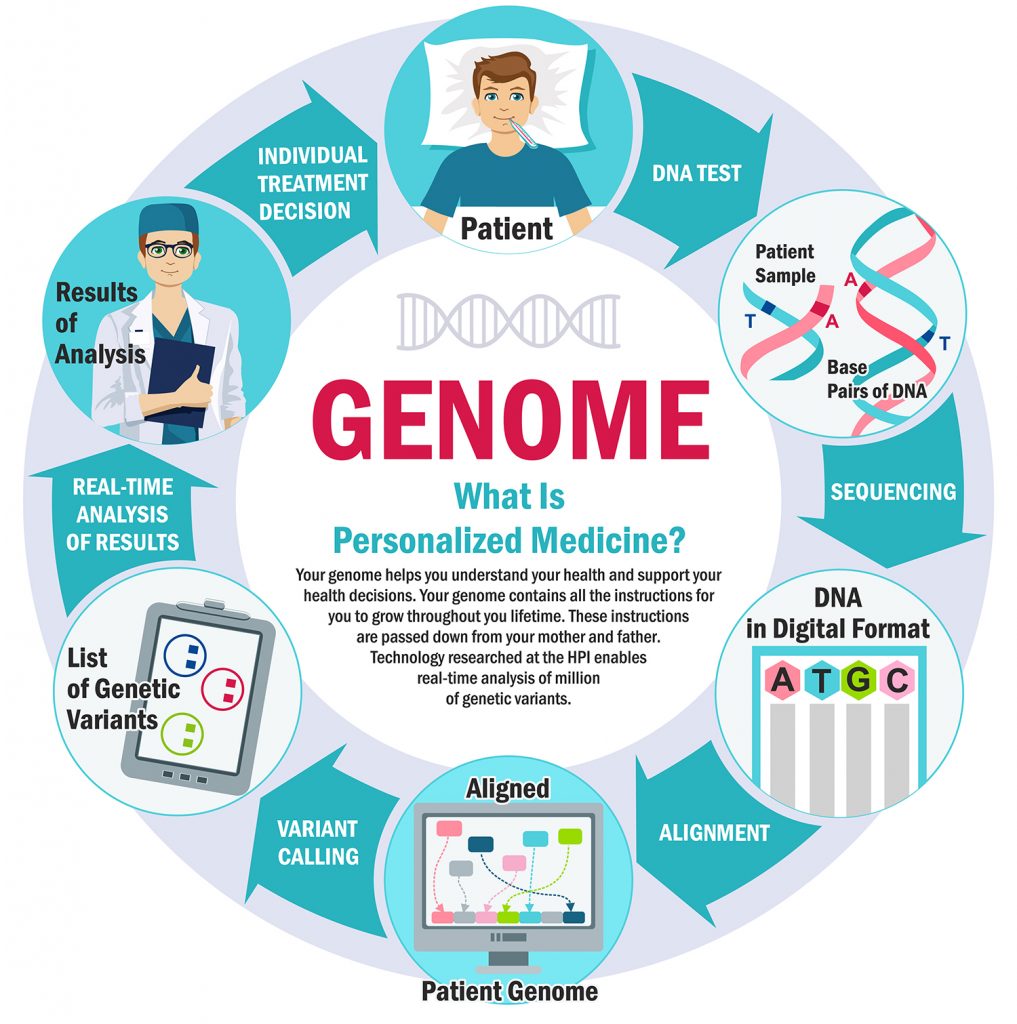
In recent years, the field of personalized medicine has gained significant traction, driven by advancements in genomics. This innovative approach tailors medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient, utilizing genetic information to enhance the effectiveness of therapies. As we delve into the topic of Personalized Medicine: How Genomics Is Shaping Healthcare’s Future, we will explore the transformative impact of genomic data on disease prevention, diagnosis, and treatment strategies. By understanding the genetic underpinnings of health, we can pave the way for more precise and effective healthcare solutions.
Throughout this article, you will discover how genomics is not only reshaping traditional medical practices but also empowering patients with personalized treatment options. We will examine the role of genetic testing in identifying predispositions to various diseases, enabling proactive healthcare measures. Additionally, we will highlight groundbreaking research and case studies that illustrate the successful implementation of genomic medicine in clinical settings. This exploration will provide you with insights into the future of healthcare, where treatments are customized to fit the unique genetic makeup of each individual.
As we navigate through the complexities of personalized medicine, we invite you to join us on this enlightening journey. By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of how genomics is revolutionizing healthcare and the potential it holds for improving patient outcomes. Stay with us as we uncover the exciting developments in this rapidly evolving field and what they mean for the future of medicine.
Personalized medicine, often referred to as precision medicine, is revolutionizing the healthcare landscape by tailoring medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient. At the core of this transformation is genomics, the study of the complete set of DNA within an organism, which provides critical insights into how genetic variations influence health and disease. This article explores various aspects of personalized medicine and its implications for the future of healthcare.
The Role of Genomics in Disease Prevention
Genomics plays a pivotal role in disease prevention by identifying genetic predispositions to various health conditions. Through genomic testing, individuals can learn about their risk factors for diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and heart disease. This knowledge empowers patients to make informed lifestyle choices and engage in preventive measures, potentially reducing the incidence of these diseases.
Moreover, early detection of genetic markers can lead to proactive monitoring and intervention strategies. For instance, individuals with a family history of breast cancer may opt for regular screenings or preventive surgeries, significantly improving their chances of survival. As genomic technologies advance, the ability to predict and prevent diseases will become increasingly precise and accessible.
Tailoring Treatments to Genetic Profiles
One of the most significant advancements in personalized medicine is the ability to tailor treatments based on an individual’s genetic profile. Pharmacogenomics, the study of how genes affect a person’s response to drugs, allows healthcare providers to prescribe medications that are more effective and have fewer side effects. This approach minimizes the trial-and-error method traditionally used in prescribing medications.
For example, patients with certain genetic variations may metabolize drugs differently, leading to variations in efficacy and safety. By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, doctors can select the most appropriate medication and dosage, enhancing treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction. This shift towards personalized treatment plans marks a significant departure from the one-size-fits-all approach in medicine.
Genomic Data and Electronic Health Records
The integration of genomic data into electronic health records (EHRs) is a crucial step towards realizing the full potential of personalized medicine. By incorporating genetic information into EHRs, healthcare providers can access a comprehensive view of a patient’s health, enabling more informed decision-making. This integration facilitates the identification of patients who may benefit from specific genomic tests or targeted therapies.
Furthermore, as more genomic data is collected and analyzed, patterns and correlations will emerge, leading to improved understanding of disease mechanisms and treatment responses. This data-driven approach not only enhances individual patient care but also contributes to broader public health initiatives by identifying trends and risk factors within populations.
Ethical Considerations in Genomic Medicine
As personalized medicine continues to evolve, ethical considerations surrounding genomic testing and data usage become increasingly important. Issues such as privacy, consent, and potential discrimination based on genetic information must be addressed to ensure that patients feel safe and secure in sharing their genomic data. The potential for misuse of genetic information raises concerns about how this data is stored, shared, and utilized.
Healthcare providers and policymakers must establish clear guidelines and regulations to protect patients’ rights while promoting the responsible use of genomic data. Engaging patients in discussions about the implications of genomic testing and ensuring informed consent are essential steps in fostering trust and transparency in personalized medicine.
The Impact of Genomics on Cancer Treatment
Genomics has profoundly impacted cancer treatment by enabling the development of targeted therapies that specifically address the genetic mutations driving tumor growth. By analyzing the genetic makeup of a patient’s tumor, oncologists can identify specific mutations and select treatments that are more likely to be effective. This approach not only improves treatment outcomes but also reduces the likelihood of unnecessary side effects associated with traditional chemotherapy.
For instance, targeted therapies such as trastuzumab for HER2-positive breast cancer have transformed the treatment landscape, offering patients more effective options. As research continues to uncover new genetic targets, the arsenal of personalized cancer therapies will expand, providing hope for patients with previously untreatable forms of cancer.
Genomic Testing and Family Planning
Genomic testing is becoming an essential tool in family planning, allowing prospective parents to assess their risk of passing on genetic disorders to their children. Carrier screening tests can identify whether individuals carry genes for inherited conditions such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell disease. This information is invaluable for couples considering starting a family, as it enables them to make informed reproductive choices.
Additionally, advancements in preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) allow for the selection of embryos free from specific genetic disorders during in vitro fertilization (IVF). This technology not only reduces the risk of genetic diseases but also provides peace of mind for parents, contributing to healthier future generations.
The Future of Genomic Research
The future of genomic research holds immense promise for advancing personalized medicine. As technology continues to evolve, the cost of genomic sequencing is decreasing, making it more accessible to a broader population. Large-scale genomic studies, such as the Human Genome Project, have paved the way for understanding the genetic basis of diseases and developing targeted therapies.
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in genomic research is expected to accelerate discoveries and enhance predictive modeling. By analyzing vast amounts of genomic data, researchers can identify new biomarkers and therapeutic targets, ultimately leading to more effective and personalized treatment options for patients.
Challenges and Limitations of Personalized Medicine
Despite the advancements in personalized medicine, several challenges and limitations remain. One significant hurdle is the need for comprehensive genomic databases that include diverse populations. Many existing databases are underrepresented, which can lead to disparities in the effectiveness of personalized treatments across different demographic groups.
Additionally, the complexity of genetic interactions and the influence of environmental factors on health outcomes complicate the development of personalized treatment plans. Ongoing research and collaboration among scientists, healthcare providers, and policymakers are essential to address these challenges and ensure that the benefits of personalized medicine are accessible to all patients.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Personalized medicine is a medical model that tailors healthcare, with decisions and treatments customized to the individual patient based on their genetic profile. |
| Role of Genomics | Genomics plays a crucial role in personalized medicine by analyzing an individual’s DNA to identify genetic variations that may influence health and disease. |
| Benefits | Benefits include improved diagnosis, targeted therapies, reduced side effects, and enhanced prevention strategies tailored to individual risk factors. |
| Applications | Applications of personalized medicine include oncology (cancer treatment), pharmacogenomics (drug response), and rare genetic disorders. |
| Challenges | Challenges include ethical concerns, data privacy issues, the need for extensive research, and the integration of genomic data into clinical practice. |
| Future Prospects | The future of personalized medicine looks promising with advancements in technology, increased understanding of genomics, and the potential for more widespread adoption in healthcare systems. |
This HTML document provides a structured overview of personalized medicine and its relationship with genomics, formatted as a table for clarity.