The Future Of Global Trade Agreements is a topic of great importance in today’s interconnected world. As countries become increasingly reliant on each other for trade and economic growth, the need for effective and fair trade agreements has become more crucial than ever. The Future Of Global Trade Agreements will shape the way countries conduct business with one another, impacting everything from tariffs and quotas to intellectual property rights and environmental standards. The evolution of these agreements will also have far-reaching effects on the global economy and the geopolitical landscape.
One alternative keyword for The Future Of Global Trade Agreements is “international trade pacts”. These pacts are crucial for facilitating the flow of goods and services between countries, and they are often the subject of heated debate and negotiation. Another important aspect to consider is the “impact of digital trade” on global trade agreements. As technology continues to advance, the rules and regulations governing digital trade are becoming increasingly important in global trade agreements. Additionally, the “role of emerging economies” in shaping the future of global trade agreements is a key point of interest. These economies are becoming major players in the global market, and their influence on trade agreements cannot be underestimated. Lastly, the “trend towards regional trade agreements” is an important factor to consider. As countries seek to strengthen trade ties with their neighbors, regional agreements may become more prevalent in the future.
The Evolution of Global Trade Agreements
Global trade agreements have evolved significantly over the years, adapting to changes in the global economy and geopolitical landscape. The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was one of the earliest global trade agreements, established in 1947 with the goal of reducing trade barriers and promoting economic cooperation among member countries. Over time, GATT evolved into the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 1995, which has played a central role in shaping the rules of international trade and resolving trade disputes among member countries.
In recent years, there has been a shift towards regional trade agreements, such as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP). These agreements involve a smaller group of countries and focus on reducing trade barriers within a specific region, leading to a more complex and fragmented global trade landscape.
The Impact of Technology on Global Trade Agreements
Advancements in technology have significantly impacted global trade agreements, transforming the way goods and services are traded across borders. The rise of e-commerce has led to new challenges and opportunities for global trade, prompting discussions on the digital economy and the regulation of online trade. Additionally, technological advancements in areas such as logistics, communication, and finance have enabled greater efficiency and transparency in global trade, influencing the terms and conditions of trade agreements.
Furthermore, the growing importance of intellectual property rights and data protection in the digital age has become a key consideration in modern trade agreements. As technology continues to advance, global trade agreements will need to adapt to the evolving landscape of the digital economy, ensuring that regulations remain relevant and effective.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations in Global Trade Agreements
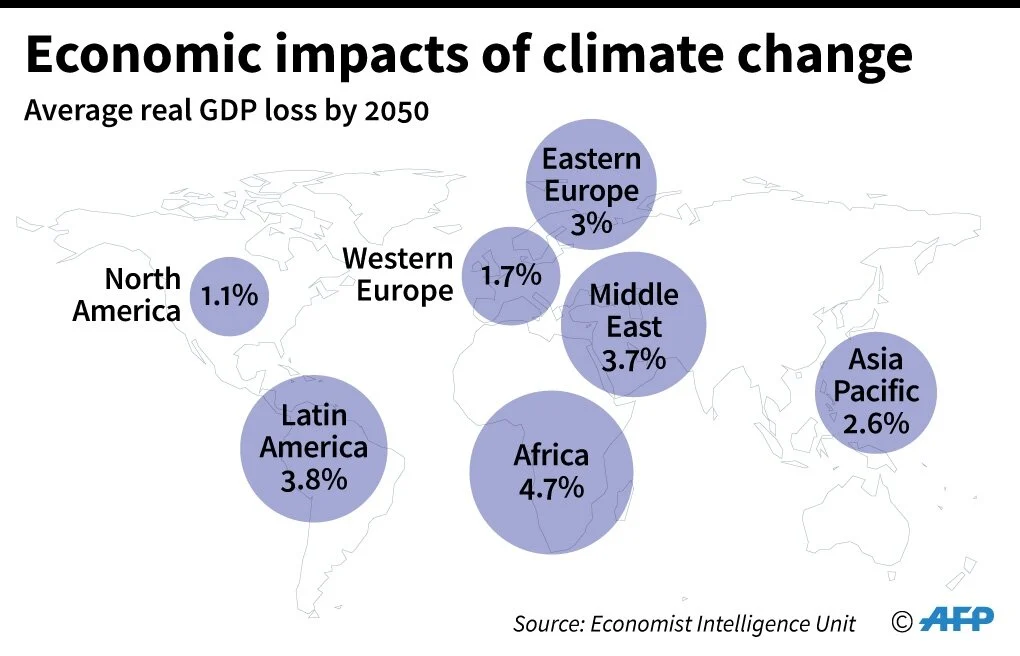
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on integrating sustainability and environmental considerations into global trade agreements. This includes discussions on the impact of trade on climate change, the conservation of natural resources, and the promotion of sustainable practices in production and consumption. As a result, modern trade agreements often include provisions related to environmental protection, sustainable development, and the enforcement of international environmental standards.
Furthermore, the concept of “green trade” has emerged, focusing on the trade of eco-friendly products and services, as well as the promotion of renewable energy and clean technologies. Integrating sustainability and environmental considerations into global trade agreements has become increasingly important, reflecting the global community’s commitment to addressing environmental challenges through international cooperation.
The Role of Geopolitics in Shaping Global Trade Agreements
Geopolitical factors have always played a significant role in shaping global trade agreements, influencing the dynamics of international trade and economic cooperation. The shifting power dynamics among major economies, regional conflicts, and diplomatic relations all have an impact on the negotiation and implementation of trade agreements. Additionally, geopolitical tensions and strategic alliances can influence the terms and conditions of trade agreements, as countries seek to advance their national interests and geopolitical objectives through trade relations.
Furthermore, geopolitical considerations can also lead to the formation of trade blocs and alliances, as seen in initiatives such as the Belt and Road Initiative and the European Union. These regional integration efforts are often driven by geopolitical motivations, aiming to strengthen economic ties and geopolitical influence among member countries.
The Future of Multilateral Trade Agreements
The future of multilateral trade agreements, such as those facilitated by the WTO, remains a topic of debate and speculation. While multilateral agreements provide a comprehensive framework for international trade, the challenges of reaching consensus among a large and diverse group of countries have led to a slowdown in the negotiation of new multilateral trade deals. However, there is ongoing discussion about the potential revival and reform of the multilateral trading system to address contemporary trade challenges.
Key issues for the future of multilateral trade agreements include addressing the concerns of developing countries, integrating new areas of trade such as digital commerce and services, and finding common ground on contentious issues such as agricultural subsidies and intellectual property rights. The future of multilateral trade agreements will likely depend on the ability of member countries to adapt to the changing global economic landscape and demonstrate a commitment to cooperative and inclusive trade policies.
The Rise of Regional Trade Agreements
In recent years, there has been a proliferation of regional trade agreements, with countries opting for more targeted and region-specific trade arrangements. These agreements, such as the CPTPP and RCEP, allow participating countries to focus on reducing trade barriers within a specific geographic area, leading to deeper integration and cooperation among member countries. Regional trade agreements offer flexibility and customization, catering to the unique economic and geopolitical dynamics of the participating countries.
Furthermore, regional trade agreements can serve as building blocks for broader multilateral trade agreements, as seen in the case of the European Union, which began as a regional trade bloc and evolved into a significant global economic and political entity. The rise of regional trade agreements reflects the shifting dynamics of global trade, with countries increasingly pursuing tailored and strategic trade arrangements to advance their economic interests.
The Impact of Trade Wars and Protectionism
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of trade wars and protectionist measures among major economies, leading to heightened tensions and disruptions in global trade. The imposition of tariffs, trade barriers, and retaliatory measures has created uncertainty and instability in the global trading system, impacting supply chains, investment decisions, and consumer prices. Trade wars and protectionism have led to a reevaluation of existing trade agreements and a reassertion of national economic interests.
Furthermore, the rise of protectionist sentiments and nationalist policies has challenged the principles of free trade and economic globalization, prompting discussions on the future of global trade agreements. The impact of trade wars and protectionism on global trade agreements underscores the need for dialogue and cooperation among countries to address trade disputes and promote a rules-based international trading system.
The Role of Public-Private Partnerships in Shaping Trade Agreements
Public-private partnerships have increasingly played a role in shaping trade agreements, as governments seek to engage with the private sector in trade negotiations and policy development. The involvement of businesses, industry associations, and non-governmental organizations in trade discussions has led to more comprehensive and inclusive trade agreements, incorporating the perspectives and interests of various stakeholders. Public-private partnerships also contribute to the implementation and enforcement of trade agreements, as businesses play a key role in adhering to trade regulations and standards.
Furthermore, public-private partnerships have been instrumental in addressing emerging trade issues, such as digital trade, sustainable development, and corporate social responsibility. The collaboration between the public and private sectors in shaping trade agreements reflects a growing recognition of the interconnectedness of economic, social, and environmental factors in global trade, and the importance of engaging diverse stakeholders in trade policy decisions.
| Agreement Name | Description | Participating Countries |
|---|---|---|
| Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) | A trade agreement among 12 Pacific Rim countries | United States, Japan, Malaysia, Vietnam, Singapore, Brunei, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, Mexico, Chile, Peru |
| Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) | A proposed free trade agreement between 15 Asia-Pacific countries | China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia, New Zealand, and 8 other ASEAN member states |
| United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) | A trade agreement between the United States, Mexico, and Canada | United States, Mexico, Canada |