Understanding The Impact Of Interest Rates On Stock Market Performance is crucial for investors and financial analysts alike. Interest rates play a significant role in shaping the economic landscape, influencing everything from consumer spending to corporate investment. As central banks adjust interest rates to manage inflation and stimulate growth, the ripple effects can be felt across the stock market. This article delves into the intricate relationship between interest rates and stock market dynamics, providing insights that can help you navigate your investment strategies more effectively.
In the following sections, we will explore how rising and falling interest rates affect stock valuations, investor sentiment, and overall market trends. You will learn about the mechanisms through which interest rates impact corporate earnings and the cost of capital, as well as how these factors can lead to shifts in market performance. Additionally, we will discuss historical examples that illustrate these concepts, giving you a clearer picture of how interest rate changes have influenced stock markets in the past.
Whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting your financial journey, understanding the impact of interest rates on stock market performance is essential. By the end of this article, you will be equipped with the knowledge to make informed investment decisions and better anticipate market movements. So, read on to uncover the vital connections between interest rates and stock market performance, and empower yourself with the insights needed to thrive in the ever-changing financial landscape.
Interest rates play a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape, influencing various sectors, including the stock market. Understanding how changes in interest rates affect stock market performance is essential for investors and policymakers alike. This article delves into several key aspects of this relationship.
Understanding Interest Rates
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money and the return on savings. They are determined by central banks and can fluctuate based on economic conditions. When interest rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can lead to reduced consumer spending and business investment. Conversely, lower interest rates can stimulate economic activity by making loans more affordable.
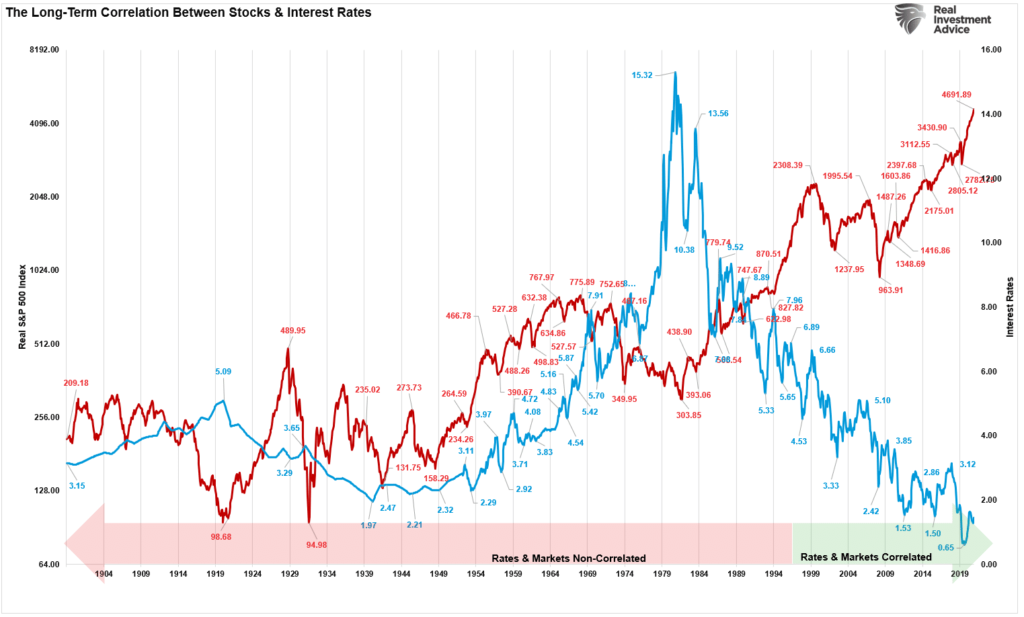
The relationship between interest rates and the stock market is complex. Investors often react to changes in interest rates by adjusting their portfolios, which can lead to volatility in stock prices. Understanding the fundamentals of interest rates is crucial for grasping their impact on stock market performance.
The Inverse Relationship Between Interest Rates and Stock Prices
Historically, there has been an inverse relationship between interest rates and stock prices. When interest rates increase, the cost of capital rises, leading to lower corporate profits and, consequently, declining stock prices. This phenomenon is particularly evident in sectors that rely heavily on borrowing, such as real estate and utilities.
On the other hand, when interest rates decrease, companies can borrow at lower costs, potentially increasing their profitability. This often results in higher stock prices as investors anticipate better earnings. Understanding this dynamic is vital for investors looking to navigate the stock market effectively.
The Role of Central Banks
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, play a significant role in setting interest rates. Their monetary policy decisions can have immediate and far-reaching effects on the stock market. For instance, when a central bank signals a rate hike, it can lead to a sell-off in stocks as investors adjust their expectations for future growth.
Conversely, when central banks lower interest rates or implement quantitative easing, it can boost investor confidence and lead to a rally in stock prices. Monitoring central bank announcements and understanding their implications is crucial for investors aiming to make informed decisions in the stock market.
Sector-Specific Impacts
Different sectors of the economy react differently to changes in interest rates. For example, financial institutions, such as banks, often benefit from rising interest rates as they can charge more for loans. In contrast, sectors like technology may suffer as higher rates can dampen consumer spending on discretionary items.
Investors should consider sector-specific dynamics when evaluating the impact of interest rates on stock market performance. A diversified portfolio that accounts for these differences can help mitigate risks associated with interest rate fluctuations.
The Impact on Consumer Spending
Interest rates directly influence consumer spending, which is a significant driver of economic growth. When rates are low, consumers are more likely to take out loans for big-ticket items, such as homes and cars. This increased spending can boost corporate earnings and, in turn, stock prices.
However, when interest rates rise, consumers may cut back on spending due to higher borrowing costs. This reduction in consumer demand can negatively impact corporate profits and lead to a decline in stock prices. Understanding this relationship is essential for investors looking to predict market trends.
Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation and interest rates are closely linked. Central banks often raise interest rates to combat rising inflation, which can have a cooling effect on the economy. Higher interest rates can lead to lower consumer spending and investment, ultimately impacting stock market performance.
Investors should keep an eye on inflation trends and central bank responses, as these factors can significantly influence market dynamics. A thorough understanding of the interplay between inflation and interest rates can provide valuable insights for investment strategies.
Historical Trends and Case Studies
Examining historical trends can provide valuable insights into the relationship between interest rates and stock market performance. For instance, during periods of rising interest rates in the late 1970s and early 1980s, the stock market experienced significant volatility and downturns.
Case studies of specific market events can illustrate how interest rate changes have historically impacted stock prices. Analyzing these trends can help investors make more informed decisions based on past performance and current economic conditions.
Strategies for Investors
Given the impact of interest rates on stock market performance, investors should develop strategies to navigate these fluctuations. Diversification across sectors, monitoring central bank policies, and staying informed about economic indicators can help mitigate risks associated with interest rate changes.
Additionally, investors may consider adjusting their portfolios in response to anticipated interest rate movements. By being proactive and informed, investors can better position themselves to capitalize on opportunities in the stock market.
Interest rates play a crucial role in the economy and have a significant impact on stock market performance. This summary outlines the key effects of interest rate changes on the stock market.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost of Borrowing | Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for companies, which can lead to reduced capital expenditures and lower growth prospects. |
| Consumer Spending | Increased interest rates can lead to higher loan and mortgage costs, reducing disposable income and consumer spending, which negatively affects company revenues. |
| Investment Appeal | As interest rates rise, fixed-income investments (like bonds) become more attractive compared to stocks, leading to potential capital outflows from the stock market. |
| Valuation Models | Higher interest rates can lead to lower present value calculations for future cash flows, resulting in lower stock valuations. |
| Market Sentiment | Changes in interest rates can influence investor sentiment and market psychology, leading to increased volatility in stock prices. |
| Sector Impact | Certain sectors, such as utilities and real estate, are more sensitive to interest rate changes, often experiencing greater fluctuations in stock prices. |
In conclusion, interest rates are a vital factor influencing stock market performance. Investors should closely monitor interest rate trends and central bank policies to make informed investment decisions.